Hello, Rubyist! Are looking for good ruby gem for interactive data
visualization? Then you must try daru-view, a plugin gem for daru.
What makes daru-view different ?
daru-viewis designed for interactive plotting of charts and tables.It provide different plotting tools like Nyaplot, HighCharts, GoogleCharts, DataTable. So you don’t have to write any JavaScript code from these sites and no need to shift to other language to get charts.It can work with any ruby web application framework like Rails/Sinatra/Nanoc/Hanami. If you want to try few examples then please look into the
daru-view/spec/dummy_*examples of Rails, Sinatra, Nanoc web applications.Now Ruby developers are using IRuby notebook for interactive programming.
daru-viewsupport IRuby notebook as well. So if you just want to see chart for some DataFrame or Array of data, you can usedaru-view.daru-viewcan generate chart images to download and save.daru-viewadaptersgooglecharts,highchartsare able to geneate 3D charts as well.Tablehave some main features like pagination, search and many more to be added.It is designed to load large data set smoothly.
Introduction
Daru is doing pretty good work as the data analysis & manipulation in IRuby notebook as well as backend part of web application. Ruby web application frameworks like Ruby on Rails, Sinatra, Nanoc are popular frameworks. So if Ruby developers get the gem like daru which can do data analysis and visualization work in applications, then there is no need of shifting to another language or usage of other gem.
My project for GSoC 2017 was to “make Daru more ready for integration with modern Web framework” in terms of visualization.
To improve in terms of viewing data, daru-view, a plugin gem for daru is created. daru-view is for easy and interactive plotting in web application & IRuby notebook. It can work in frameworks like Rails, Sinatra, Nanoc and hopefully in others too.
To see a quick overview of daru-view’s features, have a look at these examples:
Examples
This is how we can create a Plot class object:
1
| |
datacan beDaru::DataFrame, data array or the format that the adapter support.optionsis a hash that contains various options to customize the chart. If you have chosen a plotting library then you must use the options according to the options the library providing. Here is the librarydaru-viewuses. Please check the examples options, they are passing in javascript code:GoogleCharts: https://developers.google.com/chart/interactive/docs/gallery
HighCharts: https://www.highcharts.com/demo
Nyaplot: https://github.com/SciRuby/nyaplot (it works same as
daru)
Note: User must have some knowledge about the plotting tool(that you want to
use) to use it in daru-view. So that you can pass the correct options.
GoogleCharts:
Set the plotting library to :googlecharts to use this adapter. This will
load the required js files in your webpage or IRuby notebook.
1 2 | |
Let’s create a DataFrame :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
Now time to plot it:
1 2 | |
This will return the chart object we created using GoogleCharts. In IRuby notebook, you will see this:
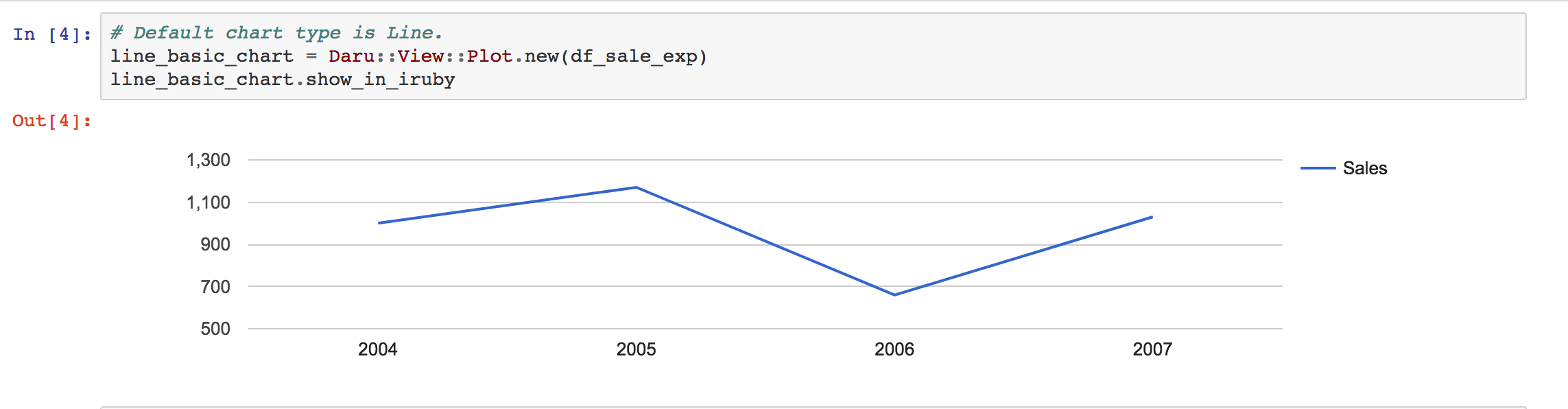
You can find the IRuby notebook example in this link.
These are various charts type we can use e.g. line, area, bar, bubble, candlestick, combo, histogram, org, pie, stepped area chart, timeline, treemap, gauge, column, scatter, etc. We can find the customization options in the google charts site.
Let me try another chart type Geo :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
Note: If you have already loaded the dependent JS files for the library then you can use adapter: :googlecharts in your Plot initialization.
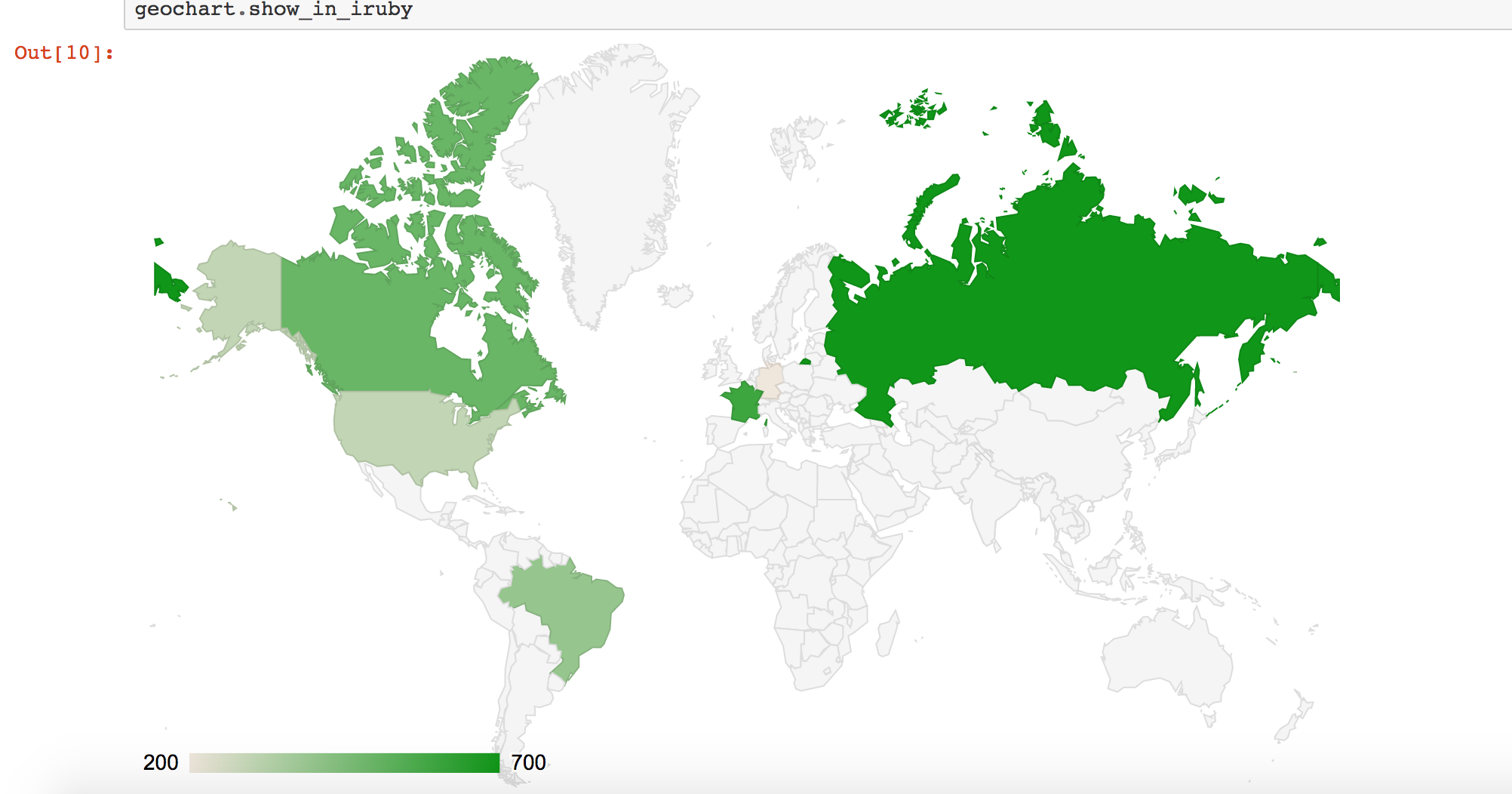
HighCharts:
Set the plotting library to :highcharts to use this adapter. This will
load the required js files in your webpage or IRuby notebook.
1 2 | |
Let’s pass the data as HighCharts support (we can pass a DataFrame as well):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | |
This will return the Plot object we created.
In IRuby notebook, you will see this:
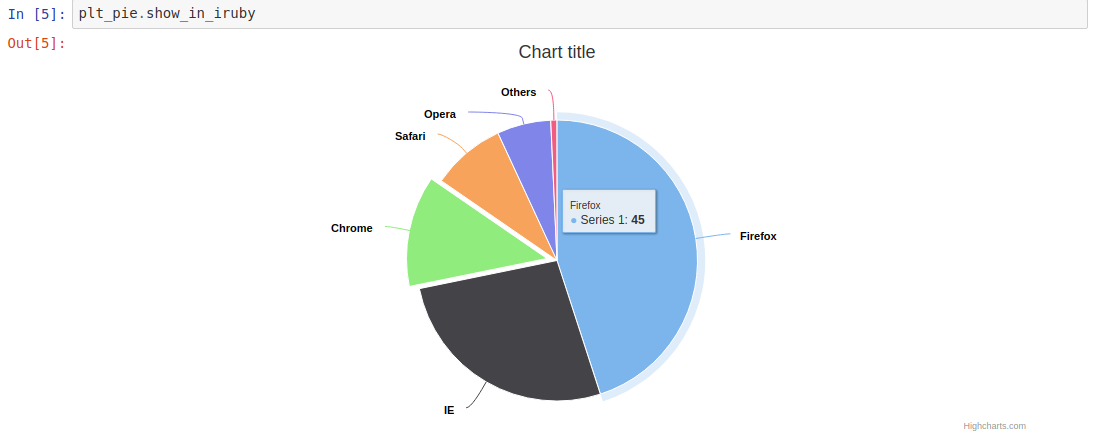
You can find the IRuby notebook example in this link.
There are various charts type we can use e.g. line, area, bar, bubble, dynamic chart, pie, column, scatter, etc. We can find the customization options in the HighCharts site.
Nyaplot
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
In IRuby notebook:
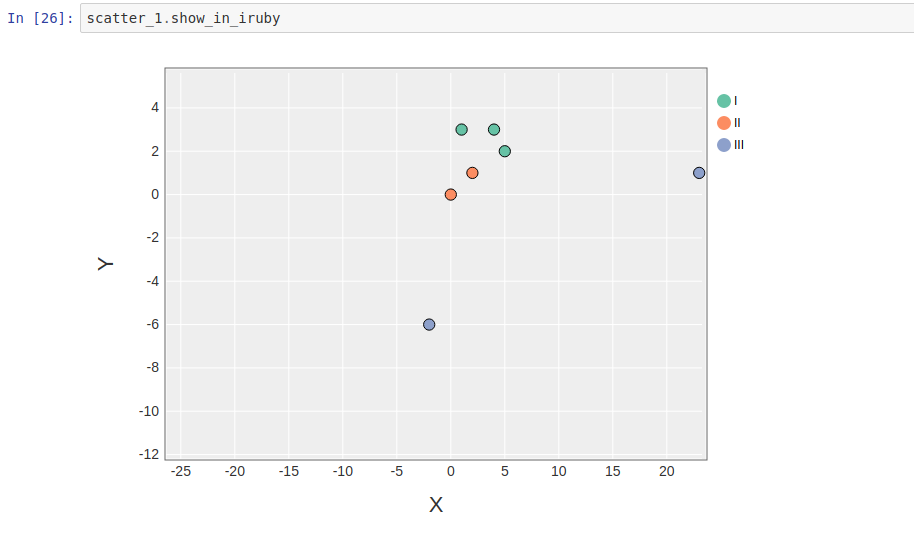
GoogleChart data table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
This will return the table object we created using GoogleCharts tool. In IRuby notebook, you will see this:
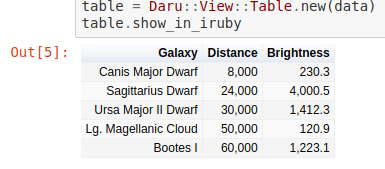
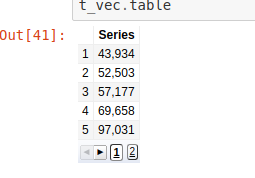
We can create table using Vectors as well.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
In Ruby Notebook:
DataTable
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
Currently there is some problem to diplay it in IRuby notebook, but in web application
you can see something like this using df_datatable.div :
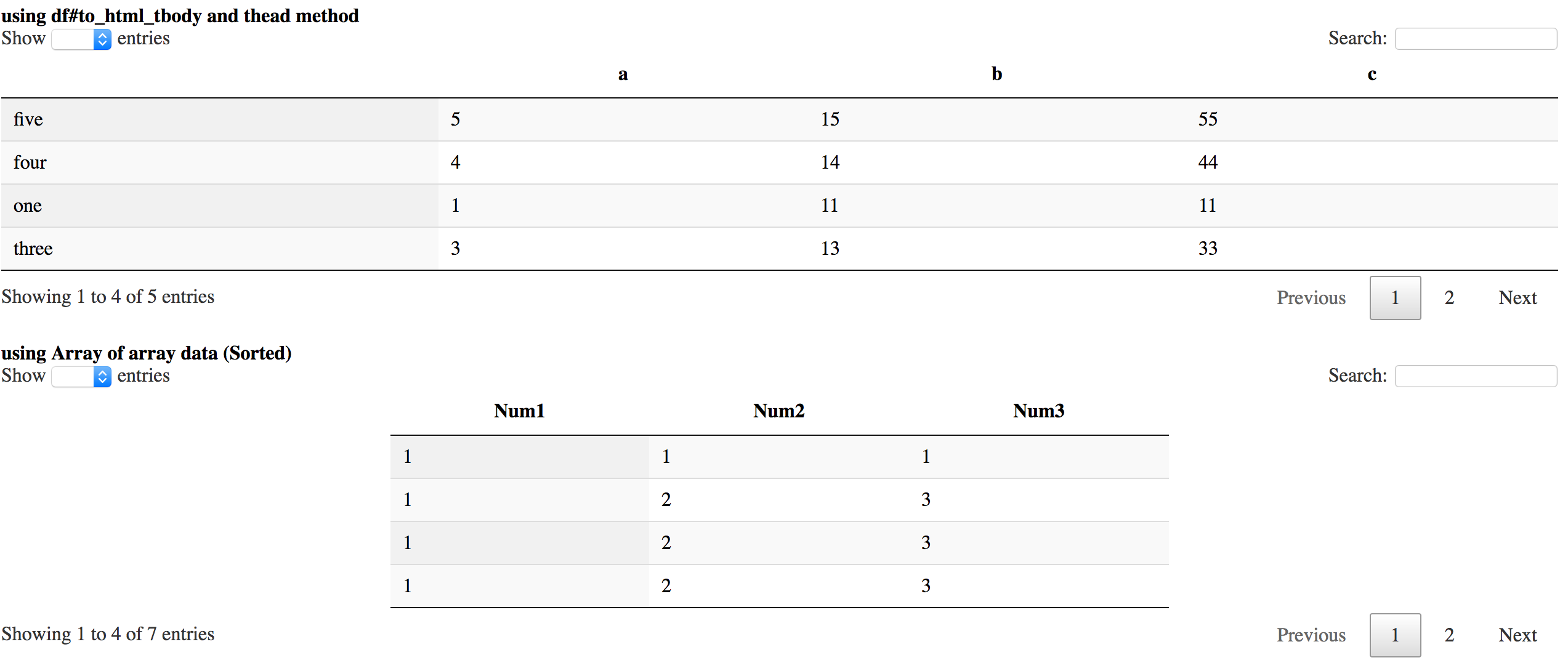
How to use it in Ruby web application
As we know, we can get the HTML, JS code for the chart from the
Daru::View::Plot or Daru:View::Table object using #div method. So just
need to add that HTML, JS code in webpage in proper place.
There is few things to be noted:
In layout of the webpage, you have to load all the dependent JS files. So that HTML, JS code that is genearted work smoothly in that webpage. You can load the dependent js file for nyaplot library using
Daru::View.dependent_script(:nyaplot), similarly for other library.If you are using multiple library in one webpage then load multiple dependent JS files, in that webpage layout (generally in head tag).
We can set default adapter using Daru::View.plotting_library = :googlecharts
and also we can change it for particular object while initializing object,
i.e. Daru::View::Plot.new(data, {adapter: :googlecharts}). Just we have
to make sure that dependent JS files are loaded for it.
To make it easy, we have defined daru_chart (that works same as Daru::View::Plot.new) , daru_table (works same as Daru::View::Table.new) for Rails application.
So you can easily use it in controller or view of the application. For reference you can check the demo Rails app.
Design of daru-view
daru-view, currently using Nyaplot, HighCharts, GoogleCharts for plotting the charts. It is also generating tables using DataTables and GoogleCharts with pagination, search and various features.
Design Pattern in daru-view
daru-view mainly uses the adapter design pattern and composite design pattern.
Why Adapter design pattern:
Adapter pattern’s motivation is that we can reuse existing gems if we can modify the interface.
daru-view joins functionalities of independent or incompatible interfaces of different gems.
daru-viewhavePlotandTableclass, which are using a adapter when adapter(library to be used for plotting) is set forPlot,Tableinstance.
Why Composite design pattern:
To define common objects and use it for defining composite objects.
In
daru-viewwe try to write common functions in a module and include it whenever needed.
Implementation
daru-view ensure that it’s functions are usable in both IRuby notebook as well as ruby web application frameworks.
The main thing we need to display something in web application or IRuby
notebook is HTML code of it. daru-view generates the HTML code of the
chart, table and the same can be used to display in web application & IRuby
notebook.
These are the libraries which is used in daru-view currently:
Nyaplot
Nyaplot is good library for
visualization in IRuby notebook only. When we use Nyaplot as the adapter in
daru-view, it is usable in both IRuby notebook and web applications. Daru
DataFrame or Vector is used as the data source of the chart. It works
similar to the initial daru plotting system.
If user want to use the Nyaplot methods then it can be done on Nyaplot object.We
can get nyplot object using daru_plot_obj.chart.
i.e.
1 2 3 | |
Now user can operate all the methods for Nyaplot object. Same thing is for all other adapter in daru-view.
HighCharts
To add the HighCharts features for plotting various chart types, daru-view uses the lazy_high_charts gem with additional features.
In this adapter data source can be Array of data, Daru::DataFrame, Daru::Vector or HTML table code of the data.
There are various of options in HighCharts. One can see the options that can be used in HighCharts demo link, which can be directly used in daru-view Plot.
HighCharts adaptor can work offline as well in daru-view. Developers can update the saved the JS files (in daru-view) using rake task automatically.
If you is familiar with lazy_high_chart gem and want to use it for
config the chart then user can access the lazy_high_chart object using
Daru::View::Plot#chart and can do necessary operations.
GoogleCharts
To add the GoogleCharts features for plotting various chart types, daru-view uses the google_visualr gem with additional features(in this module more new features are updated).
We want GoogleChart adapter to be very strong since Google chart tools always gets updated and it has amazing plotting features. Similar to the HighCharts module, here also we can use all the options described in Google Charts website.
User can access the google_visualr object using Daru::View::Plot#chart, if
they want to operate google_visualr methods.
GoogleCharts as data table
One of the good thing about google chart tool is, it can be used for generating table for web application and IRuby Notebook with pagination and other features.
Daru::View::Plot can take data Array, Daru::DataFrame, Daru::Vector,
Daru::View::Table as data source.
Daru::View::Table can take data Array, daru DataFrame, Daru Vector as data
source.
DataTables
DataTables has interaction controls to any HTML table. It can handle large set of data and have many cool features.
To use it, daru-view uses https://github.com/Shekharrajak/data_tables gem. [Note: the gem name will be changed in near future]
It basically uses the HTML table code and add features that user want. So internally HTML table code of Daru::DataFrame and Daru::Vector is passed as data source parameter.
Future Work
daru-view will be more powerful and simple in near future. Developers can add more libraries in daru-view easily, if required. To add library follow the setups given in CONTRIBUTING.md
Conclusion
The aim of the daru-view is to plot charts in IRuby notebook and ruby web application easily, so that developers need not have to use any other gem or language for visualization.
It can work smoothly in Rails/Sinatra/Nanoc web frameworks and I hope it can work in other ruby frameworks as well, because daru-view is generating the html code and javascript code for the chart, which is basic need of the webpage.
Why not use the plotting libraries directly?
If you are using daru gem for analyzing the data and want to visualize it, then it will be good if you have data-visualization within daru and can plot it directly using DataFrame/Vector objects of daru.
daru-view will be helpful in plotting charts and tables directly from the Daru::DataFrame and Daru::Vector . daru-view using nyaplot, highcharts , google charts right now to plot the chart. So user can set the plotting library and get the chart accordingly.
Most of the plotting libraries doesn’t provide the features of plotting charts in iruby notebook. They are defined only for web applications (mostly for Rails). But daru-view can plot charts in any ruby web application as well as iruby notebook.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank to my mentors Sameer Deshmukh ,Lokesh Sharma and Victor Shepelev for their response and support and I am very grateful to the Ruby Science Foundation for this golden opportunity.
I thank my fellow GSoC participants Athitya Kumar and Prasun Anand for their support and discussions on various topics.
Thanks to Google for conducting Google Summer of Code.